Background: Occlusal trauma can irritate periodontitis, however the mechanism stays unclear. Sure-associated protein (YAP), a mechanical stressor protein, could play an necessary function on this course of.
Strategies: Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain response (qRT-PCR) had been utilized to detect the expression of YAP and inflammatory elements in sufferers with periodontitis accompanied with or with out occlusal trauma. By native administration of Porphyromonas gingivalis and composite resin bonding on maxillary molars in mice, we established periodontitis and occlusal trauma fashions.
Therapy with or with out XAV939, to inhibit YAP activation, was carried out in these fashions. Micro-computed tomography, immunofluorescence (IF), and qRT-PCR had been used to discover the YAP pathway in periodontitis with occlusal trauma. Cyclic stress and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimuli had been utilized to the L929 mouse fibroblast cell line with or with out XAV939. Western blot, IF, and qRT-PCR had been used to confirm the in vivo outcomes.
Outcomes: Activated dephosphorylated YAP and elevated expression of inflammatory elements had been noticed in sufferers with periodontitis accompanied with occlusal trauma. Within the mouse mannequin of periodontitis with occlusal trauma, YAP transferred into the nucleus, leading to Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) associated pro-inflammatory pathway up-regulation. L929 cell cyclic stress and LPS stimulation outcomes confirmed the in vivo outcomes. Software of XAV939 inhibited YAP protein dephosphorylation and decreased JNK pro-inflammatory pathway issue expression in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusions: Occlusal trauma can activate YAP nuclear switch, ensuing within the up-regulation of the JNK pro-inflammatory pathway. This may be inhibited by the XAV939 YAP inhibitor. This text is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein and its penalties
- The rising novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has created a worldwide well being disaster that warrants an correct and detailed characterization of the quickly evolving viral genome for understanding its epidemiology, pathogenesis and containment. Right here, we explored 61,485 sequences of the nucleocapsid (N) protein, a potent diagnostic and prophylactic goal, for figuring out the mutations to evaluate their roles in real-timePCR based mostly analysis and observe consequent impacts.
- In comparison with the Wuhan reference pressure, a complete of 1034 distinctive nucleotide mutations had been recognized within the mutant strains (49.15%, n=30,221) globally. Of those mutations, 367 occupy primer binding websites together with 3′-end mismatch to primer-pair of 11 nicely characterised primer units. Noteworthy, CDC (USA) really useful N2 primer set contained decrease mismatch than the opposite primer units. Furthermore, 684 amino acid (aa) substitutions situated throughout 317 (75.66% of complete aa) distinctive positions together with 82, 21, and 83 of these in RNA binding N-terminal area (NTD), SR-rich area, and C-terminal dimerization area (CTD), respectively.
- Furthermore, 11 in-frame deletions, principally (n =10) throughout the extremely versatile linker area, had been revealed and the remaining throughout the NTD area. Moreover, we predicted the doable consequence of high-frequency mutations (≥ 20) and deletions on the tertiary construction of the N protein. Remarkably, we noticed that top frequency (67.94% of mutated sequences) co-occuring mutations (R203Ok and G204R) destabilized and decreased general structural flexibility.
- The N protein of SARS-CoV-2 contains a mean of 1.2 mutations per pressure in comparison with 4.Four and 0.Four in MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV, respectively. Regardless of being proposed because the alternate goal to spike protein for vaccine and therapeutics, ongoing evolution of the N protein could problem the endeavors, thus want additional immunoinformatics analyses. Subsequently, steady monitoring is required for tracing the continuing evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein in prophylactic and diagnostic interventions. This text is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.

transgenicnews
Impairment of cell adhesion and migration by inhibition of protein disulphide isomerases in three breast most cancers cell strains
- Protein disulphide isomerase A3 (PDIA3) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident disulphide isomerase and oxidoreductase with recognized substrates that embody some extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. PDIA3 is up-regulated in invasive breast cancers and correlates in a mouse orthotopic xenograft mannequin with breast most cancers metastasis to bone. Nevertheless, the underlying mobile mechanisms stay unclear.
- Right here we investigated the perform of protein disulphide isomerases in attachment, spreading and migration of three human breast most cancers strains consultant of luminal (MCF-7) or basal (MDA-MB-231 and HCC1937) tumour phenotypes. Pharmacological inhibition by 16F16 decreased preliminary cell spreading extra successfully than inhibition by PACMA-31. Cells displayed diminished cortical F-actin projections, stress fibres and focal adhesions. Cell migration was decreased in a quantified ‘scratch wound’ assay.
- To look at whether or not these results may outcome from alterations to secreted proteins within the absence of practical PDIA3, adhesion and migration had been quantified within the above cells uncovered to media conditioned by wildtype (WT) or Pdia3-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). The conditioned medium (CM) of Pdia3-/- MEFs was much less efficient in selling cell spreading and F-actin organisation or supporting ‘scratch wound’ closure.
- Equally, ECM ready from HCC1937 cells after 16F16 inhibition was much less efficient than management ECM to assist spreading of untreated HCC1937 cells. Total, these outcomes advance the idea that protein disulphide isomerases together with PDIA3 drive the manufacturing of secreted proteins that promote a microenvironment beneficial to breast most cancers cell adhesion and motility, traits which can be integral to tumour invasion and metastasis. Inhibition of PDIA3 or associated isomerases could have potential for anti-metastatic therapies.
Host Plant Methods to Fight Towards Viruses Effector Proteins
Viruses are obligate parasites that exist in an inactive state till they enter the host physique. Upon entry, viruses turn into lively and begin replicating through the use of the host cell equipment. All plant viruses can increase their transmission, thus powering their detrimental results on the host plant.
To decrease an infection and ailments brought on by viruses, the plant has a defence mechanism often called pathogenesis-related biochemicals, that are metabolites and proteins. Proteins that finally stop pathogenic ailments are known as R proteins. A number of plant R genes (that verify resistance) and avirulence protein (Avr) (pathogen Avr gene-encoded proteins [effector/elicitor proteins involved in pathogenicity]) molecules have been recognized.
The popularity of such an element leads to the plant defence mechanism. Throughout plant viral an infection, the replication and expression of a viral molecule result in a sequence of a hypersensitive response (HR) and have an effect on the host plant’s immunity (pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity and effector-triggered immunity). Avr protein renders the host RNA silencing mechanism and its innate immunity, mainly often called silencing suppressors in direction of the plant defensive equipment. This can be a robust reply to the plant defensive equipment by dangerous plant viruses.
On this evaluate, we describe the plant pathogen resistance protein and the way these proteins regulate host immunity throughout plant-virus interactions. Moreover, we’ve got mentioned relating to ribosome-inactivating proteins, ubiquitin proteasome system, translation repression (nuclear shuttle protein interacting kinase 1), DNA methylation, dominant resistance genes, and autophagy-mediated protein degradation, that are essential in antiviral defences.
 pOET 1N_6xHis transfer plasmid |
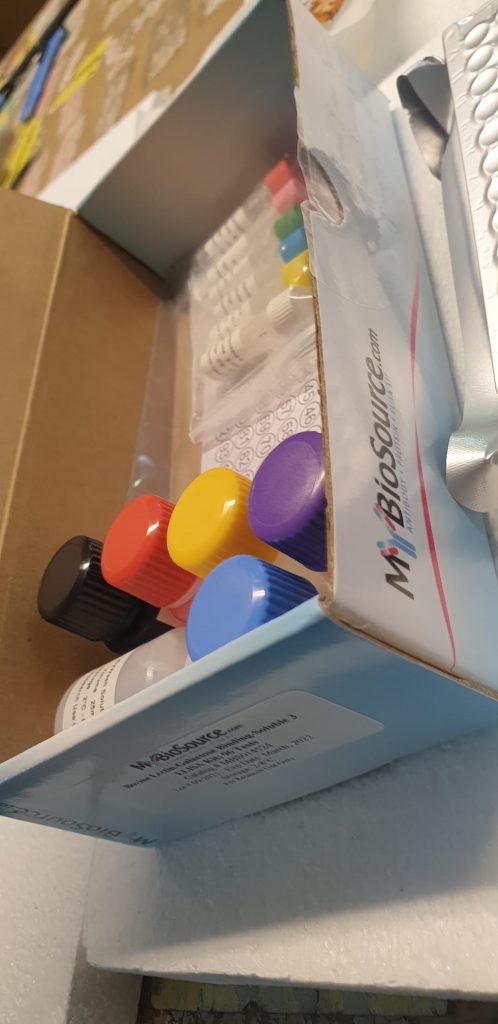
| GWB-001011 | GenWay Biotech | 10ug | Ask for price |
 pOET-2 C 6xHis transfer plasmid |
| GWB-001032 | GenWay Biotech | 10 ul | Ask for price |
 pOET 1C 6xHis transfer plasmid |
| GWB-001012 | GenWay Biotech | 10ug | Ask for price |
) pOET-5 Transfer Vector (10ug) |
| GWB-200106 | GenWay Biotech | 10 ug | Ask for price |
 pOET 2 N/C_6xHis™ Transfer Vector |
| GWB-001031 | GenWay Biotech | 10 ug | Ask for price |
) CCND1 with C-tGFP tag for Nucleus marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100009 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |
) LAMP1 with C-tGFP tag for Lysosome marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100016 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |
) LMNB1 with N-tGFP tag for Nucleus marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100018 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |
) Rab4 with N-tGFP tag for Endosome marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100025 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |
) Rab5 with N-tGFP tag for Endosome marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100026 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |
) RhoB with N-tGFP tag for Endosome marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100027 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |
) CCND1 with C-tRFP tag for Nucleus marking (10ug transfection-grade plasmid) |
| RC100041 | Origene Technologies GmbH | 10 µg | Ask for price |

)



)












)
)
)
)
)
)
)




